Bruxism (teeth grinding) treatment
Teeth grinding is the most obvious form of bruxism, which is an excessive muscular activity that results in prolonged and extremely vigorous contact between the teeth, unrelated to normal function, such as eating or talking. It usually happens at an unconscious level during sleep, but it can also occur during the daytime.

Treatment Duration
30 minutes

Price
From £800

Recovery Time
24 hours

Bruxism can become a health concern as it wears away dental substances very quickly. It can also trigger the onset of other conditions such as chronic pain, toothache, headaches, and tinnitus. It can affect people of any age.
What happens when you grind your teeth?
Firstly, it can lead to tooth wear and damage. The enamel, which is the hard outer layer of the teeth, can wear down, exposing the more sensitive dentin underneath. This can result in tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks. In severe cases, grinding can lead to cracked, chipped, or even loose teeth.
Furthermore, bruxism puts a strain on the jaw muscles and joints. This can lead to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, characterized by pain or discomfort in the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. Symptoms can include a clicking or popping sound when moving the jaw, difficulty in opening the mouth wide, and even headaches or earaches.
Chronic teeth grinding can also impact overall oral health. It may cause or exacerbate gum recession and lead to loss of bone around the teeth. In addition to physical effects, bruxism can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep disturbances both for the person grinding and their sleeping partner.
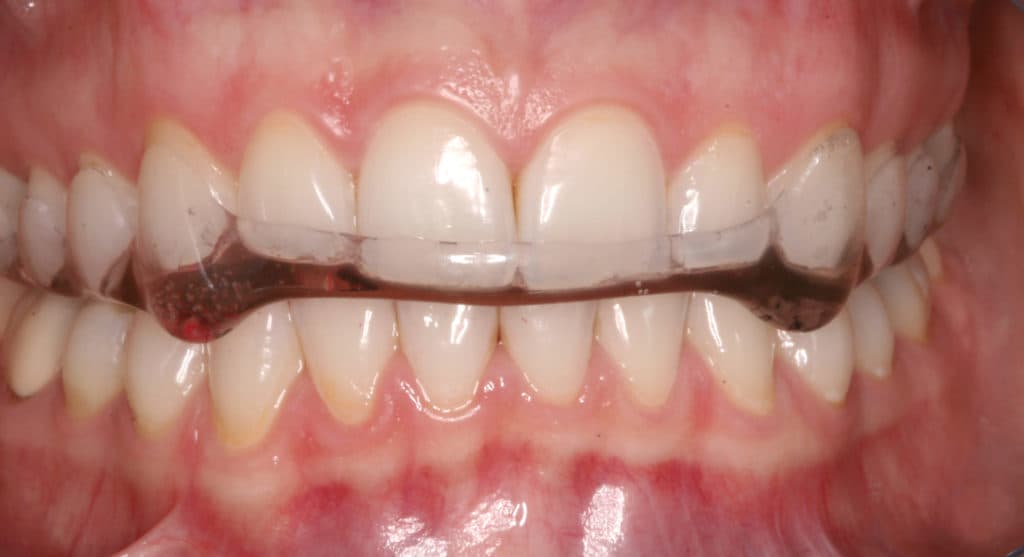
Treatment options include wearing a mouthguard at night to protect the teeth, stress management techniques, and addressing any underlying sleep disorders. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for monitoring the effects of bruxism and implementing timely interventions.
Meet your award-winning Bruxism (teeth grinding) dentist and team…
- We have over 75+ years of combined dentistry experience across our specialist team.
- 10,000+ treatments performed and counting.
- We are leaders in the dental industry – we regularly teach, lecture and publish our research work internationally.

Helen Li
Wimpole Street Dental has the highest most ethical standard of work, personable approach, clear and safe procedures, top notch excellence and reliability in treatment provided with utmost professionalism from crème de la crème world class specialists all under one roof.

New page design
Written by: Prof Dr Christian Mehl
Medically reviewed by: Dr Raul Costa
Author biography added
Written by: Prof Dr Christian Mehl
Medically reviewed by: Dr Raul Costa
Original content created
Written by: Prof Dr Christian Mehl
Medically reviewed by: Dr Raul Costa
Wimpole St Dental Clinic has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Lobbezoo F, Ahlberg J, Glaros AG, Kato T, Koyano K, Lavigne GJ, de Leeuw R, Manfredini D, Svensson P, Winocur E. Bruxism defined and graded: an international consensus. J Oral Rehabil. 2013 Jan;40(1):2-4. doi: 10.1111/joor.12011. Epub 2012 Nov 4. PMID: 23121262.
- Klasser GD, Rei N, Lavigne GJ. Sleep bruxism etiology: the evolution of a changing paradigm. J Can Dent Assoc. 2015;81:f2. PMID: 25633110.
- Mark AM. What is bruxism? J Am Dent Assoc. 2021 Sep;152(9):788. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2021.06.012. PMID: 34454650.
- Manfredini D, Ahlberg J, Lobbezoo F. Bruxism definition: Past, present, and future – What should a prosthodontist know? J Prosthet Dent. 2022 Nov;128(5):905-912. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2021.01.026. Epub 2021 Mar 5. PMID: 33678438.

























